News

A little empathy can go a long way toward ending infectious disease outbreaks. That’s a conclusion from researchers who used a networked variation of game theory to study how individual behavior during an outbreak of influenza – or other…

Researchers have successfully identified biological signatures in pediatric patients with newly diagnosed Crohn’s disease (CD) capable of predicting whether a child will develop disease-related complications requiring major surgery within three…

Raquel Lieberman has started the year with excellent news: She’s been asked to serve on the academic editorial board of a major scientific journal, and she and her research team can continue their work on early-stage glaucoma, thanks to this…

Could bacteria with aggressive weapons someday replace some antibiotics? Perhaps. Researchers are using math to predict cholera strains' effectiveness against competing cholera, as they stab and poison each other on the battlefield. Being…

Petit Institute researcher elected as councilor in American Chemistry Society

Cells have no obvious entryways for materials in their surroundings. They bring things inside by engulfing objects. Immune cells, for example, engulf pathogens, which can be larger than themselves. The process is called phagocytosis.
…

Oceanic dead zones are natural laboratories for exploring biological diversity. In a study published this year in the journal Nature, scientists at Georgia Tech discovered new species of the world's most abundant organism group, a…

A recent study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences analyzed the viral content of the human gut (Manrique et al., PNAS, 2016). The research focused on a…

Georgia Tech researchers have developed a theory to unite the study of behavior and its effect on the environment. In doing so, they combined theories of strategic behavior with those of resource depletion and restoration, leading to what…

That the right funding can focus science on longer, bigger gains becomes clear through the example of Will Ratcliff, just named a 2016 Packard Fellow. The announcement jolted his research mindset far beyond the horizons of his…

James T. “Tim” Farmer is an undergraduate researcher in the CHAOS lab in the School of Physics. Visit the lab and you might see him delicately removing the heart of a tiny fish and then bathing the fragile heart with a dye solution to help…
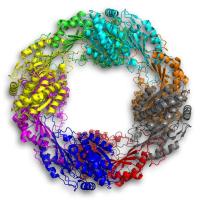
This enzyme is "wacko" in the ways it breaks down a poison related to TNT. On top of that, 5NAA-A is known so far only to exist in a single living organism on Earth -- a type of bacteria. Could it be the lone master of a rare bacterial enzymatic…

Joseph Lachance’s Georgia Tech group is one of 74 contributors worldwide

How do you benchmark something that goes back 10 or 80 million years, like simulations of ancient genes and proteins, when you don't have a time machine to travel back and check the results? There's a way. And it shows the simulations are…

Will Ratcliff tried something many scientists doubted would ever succeed. He pushed yeast to evolve in the lab from single-cell to multicellular beings. “It was a kind of Hail Mary pass,” he said. It worked, and opened up a path to sustained…

Nine graduate students launch Georgia Tech’s third interdisciplinary life sciences Ph.D.

The University System of Georgia Board of Regents has appointed Georgia Tech faculty members Seymour E. Goodman, NIcholas V. Hud, and Vladimir Tsukruk as Regents’ Professors and Alexa Harter as a Regents’ Researcher. The titles represent the…

Global warming is expanding ocean regions where oxygen has already vanished. There, newly discovered bacteria deplete waters of nitrogen, a nutrient essential to life. Though nitrogen depletion itself is natural, it appears to be expanding along…


